5.OA.1:
Operations And Algebraic Thinking
Write And Interpret Numerical Expressions.
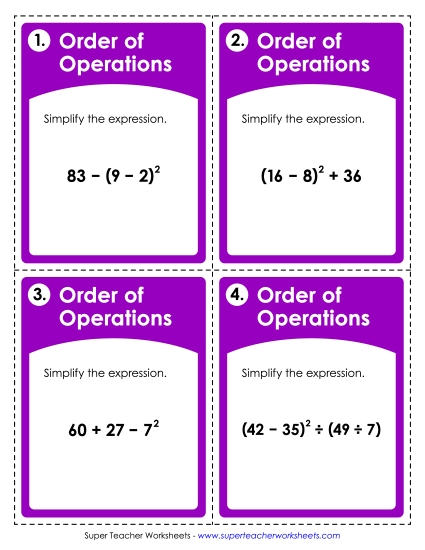
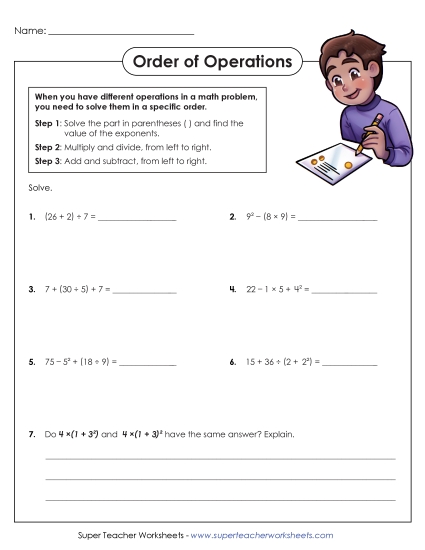
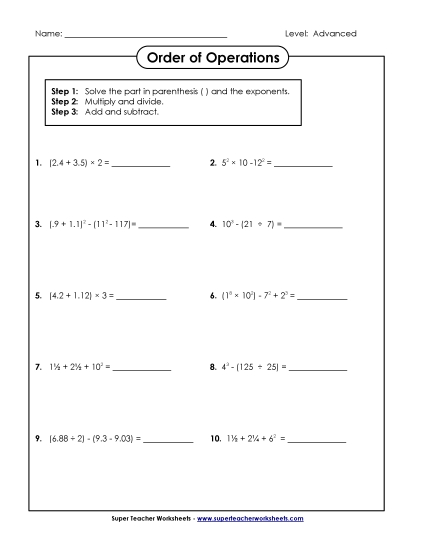
Use parentheses, brackets, or braces in numerical expressions, and evaluate expressions with these symbols.
6.EE.1:
Expressions And Equations
Apply And Extend Previous Understandings Of Arithmetic To Algebraic Expressions.
Write and evaluate numerical expressions involving whole-number exponents.
6.EE.2c:
Expressions And Equations
Apply And Extend Previous Understandings Of Arithmetic To Algebraic Expressions.
Evaluate expressions at specific values of their variables. Include expressions that arise from formulas used in real-world problems. Perform arithmetic operations, including those involving whole- number exponents, in the conventional order when there are no parentheses to specify a particular order (Order of Operations). For example, use the formulas V = s3 and A = 6 s2 to find the volume and surface area of a cube with sides of length s = 1/2.
5.OA.2:
Operations And Algebraic Thinking
Write And Interpret Numerical Expressions.
Write simple expressions that record calculations with numbers, and interpret numerical expressions without evaluating them. For example, express the calculation "add 8 and 7, then multiply by 2" as 2 x (8 + 7). Recognize that 3 x (18932 + 921) is three times as large as 18932 + 921, without having to calculate the indicated sum or product.