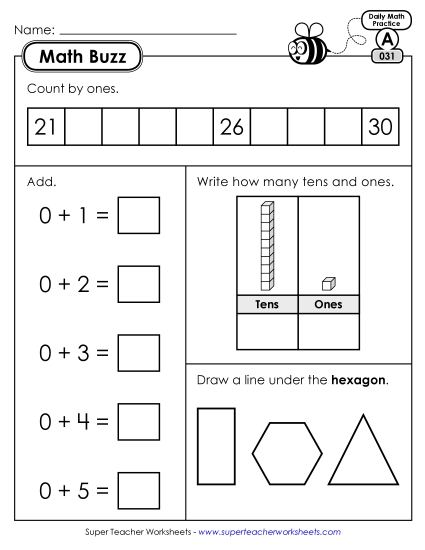
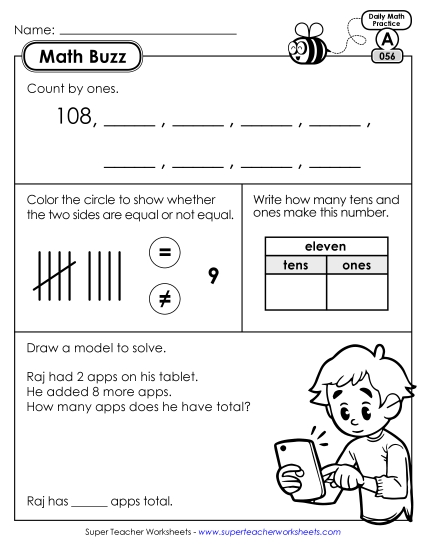
1.NBT.2:
Number And Operations In Base Ten
Understand Place Value.
Understand that the two digits of a two-digit number represent amounts of tens and ones. Understand the following as special cases:
a. 10 can be thought of as a bundle of ten ones - called a "ten."
b. The numbers from 11 to 19 are composed of a ten and one, two, three, four, five, six, seven, eight, or nine ones.
c. The numbers 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90 refer to one, two, three, four, five, six, seven, eight, or nine tens (and 0 ones).
1.NBT.2a:
Number And Operations In Base Ten
Understand Place Value.
10 can be thought of as a bundle of ten ones - called a "ten." b.
K.CC.2:
Counting And Cardinality
Know Number Names And The Count Sequence.
Count forward beginning from a given number within the known sequence (instead of having to begin at 1).
K.G.2:
Geometry
Identify And Describe Shapes (Squares, Circles, Triangles, Rectangles, Hexagons, Cubes, Cones, Cylinders, And Spheres).
Correctly name shapes regardless of their orientations or overall size.
1.OA.4:
Operations And Algebraic Thinking
Understand And Apply Properties Of Operations And The Relationship Between Addition And Subtraction.
Understand subtraction as an unknown-addend problem. For example, subtract 10 - 8 by finding the number that makes 10 when added to 8.