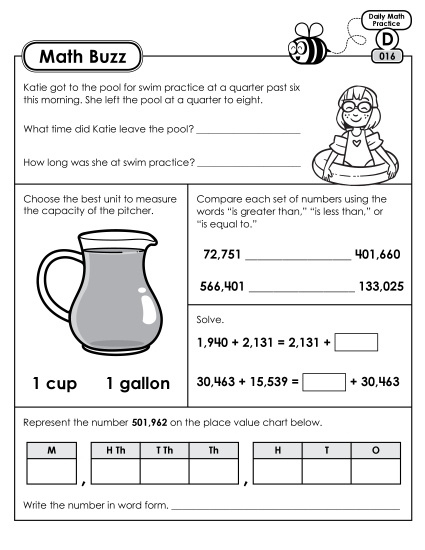
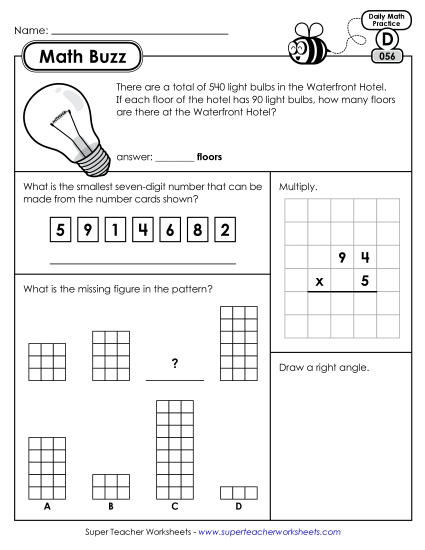
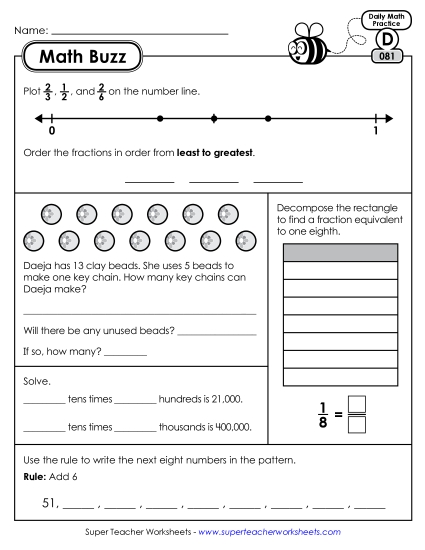
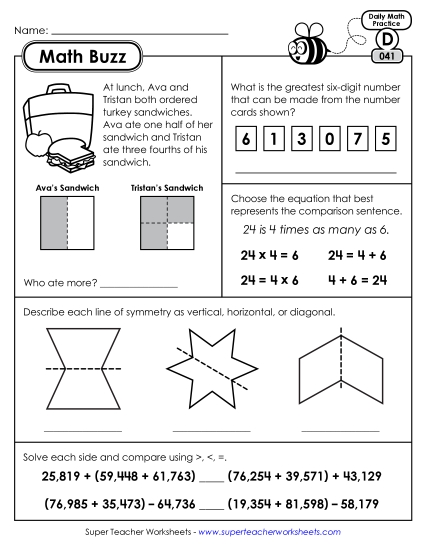
4.NBT.3:
Number And Operations In Base Ten
Generalize Place Value Understanding For Multi-Digit Whole Numbers.
Use place value understanding to round multi-digit whole numbers to any place.
4.OA.1:
Operations And Algebraic Thinking
Use The Four Operations With Whole Numbers To Solve Problems.
Interpret a multiplication equation as a comparison, e.g., interpret 35 = 5 x 7 as a statement that 35 is 5 times as many as 7 and 7 times as many as 5. Represent verbal statements of multiplicative comparisons as multiplication equations.
3.G.1:
Geometry
Reason With Shapes And Their Attributes.
Understand that shapes in different categories (e.g., rhombuses, rectangles, and others) may share attributes (e.g., having four sides), and that the shared attributes can define a larger category (e.g., quadrilaterals). Recognize rhombuses, rectangles, and squares as examples of quadrilaterals, and draw examples of quadrilaterals that do not belong to any of these subcategories.
3.MD.3:
Measurement And Data
Represent And Interpret Data.
Draw a scaled picture graph and a scaled bar graph to represent a data set with several categories. Solve one- and two-step "how many more" and "how many less" problems using information presented in scaled bar graphs. For example, draw a bar graph in which each square in the bar graph might represent 5 pets.